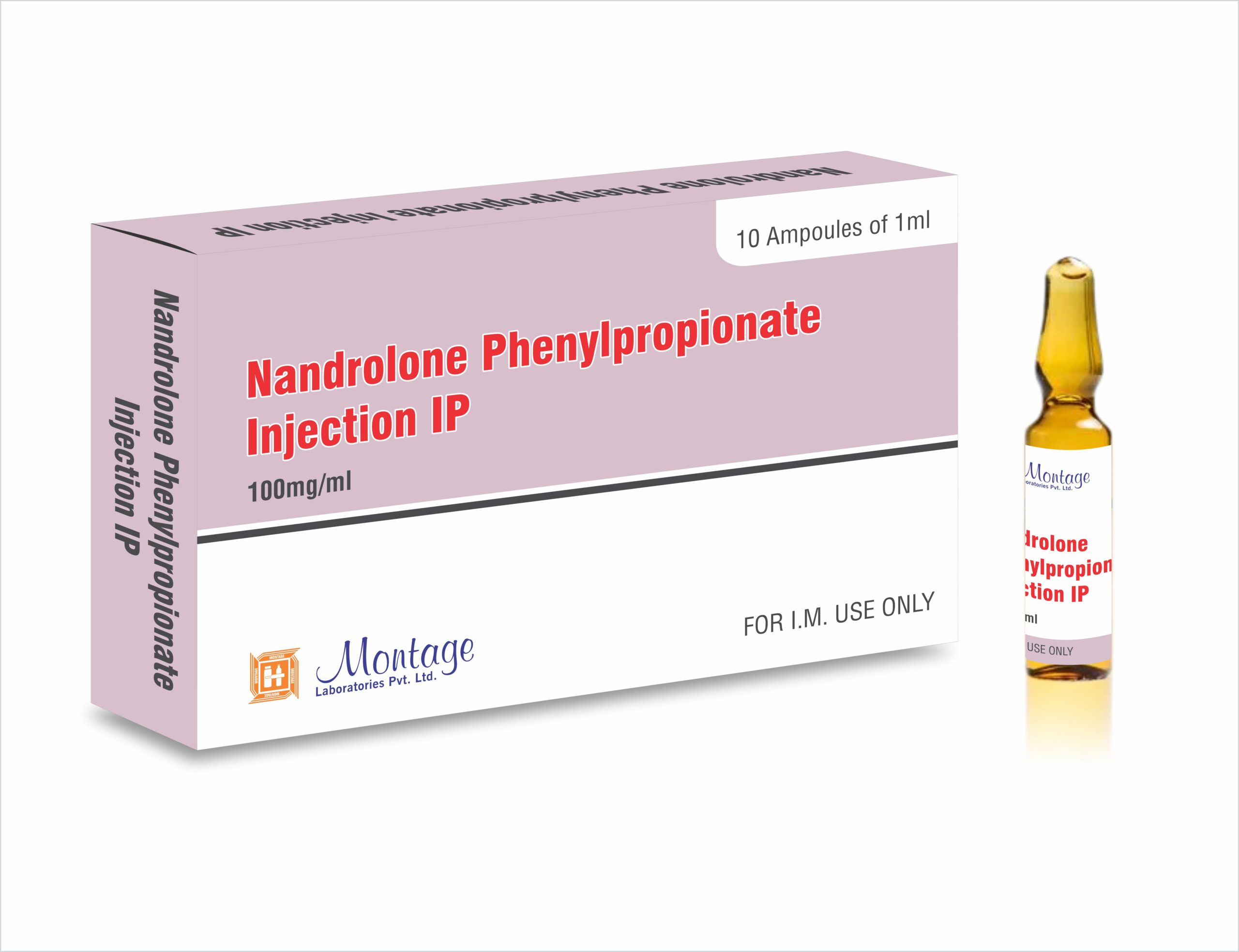
Nandrolone Phenylpropionate Anabolic Steroid for Performance and Physique
Nandrolone Phenylpropionate (NPP) is a powerful anabolic steroid that is chemically similar to testosterone, with strong anabolic effects and weaker androgenic effects. It has been used primarily for medical purposes, such as treating advanced breast cancer and osteoporosis in postmenopausal women. Due to its lower androgenic activity, NPP is less likely to cause masculinization in women compared to other steroids. However, at higher dosages, side effects like acne, voice changes, and increased hair growth may occur.
Introduced in 1959, NPP is one of the first nandrolone esters and was historically favored for its effectiveness. While it has largely been replaced by longer-acting nandrolone decanoate, NPP is still used for performance and physique enhancement by athletes, bodybuilders, and powerlifters. It has a shorter half-life compared to nandrolone decanoate, which means it needs to be injected more frequently.
Benefits
- Promotes muscle growth and improves muscle strength.
- Increases red blood cell production, enhancing endurance.
- Supports bone health by improving bone density.
- Provides a mild side effect profile, especially for women.
- Enhances recovery from intense physical activity and injury.
- Improves overall physical performance and physique for athletes and bodybuilders.
- Aids in the treatment of osteoporosis and breast cancer in women.
Usage Instructions
- NPP is administered via intramuscular injection, typically once a week.
- The recommended dosage varies depending on the individual’s health condition and goals. For medical use, dosages range from 25 mg to 100 mg per week.
- Non-medical use in bodybuilding or athletic performance should only be considered with a doctor’s guidance, as it’s regulated in many countries.
- NPP should not be used in pregnancy or breastfeeding, as it may harm the fetus or infant.
- Always consult a healthcare provider before starting or adjusting the dosage.
Ingredients and Composition
- Active Ingredient: Nandrolone Phenylpropionate
- Other Ingredients: Oil-based solvent, typically sesame oil or cottonseed oil, used for suspension and injection.
Potential Side Effects
- Virilization: In women, side effects like acne, hoarseness, deepening of the voice, and increased facial/body hair may occur, especially with higher doses or long-term use.
- Androgenic Effects: Includes symptoms like increased aggression, male-pattern hair loss, and oily skin.
- Liver toxicity (rare but possible with prolonged use).
- Water retention, which can lead to swelling and bloating.
- Cardiovascular issues, such as an increase in cholesterol levels and high blood pressure, with prolonged or high-dose use.
- Mood swings, irritability, or aggression.
Precautions and Warnings
- Pregnancy and Breastfeeding: NPP should not be used during pregnancy or while breastfeeding due to potential risks to the child.
- Liver and Kidney Function: Individuals with pre-existing liver or kidney conditions should consult a healthcare provider before using NPP.
- Heart and Cardiovascular Health: Those with cardiovascular diseases should use NPP with caution, as it may affect cholesterol and increase the risk of heart issues.
- Mental Health: NPP may cause mood changes, irritability, and aggression. Those with a history of mental health issues should be cautious.
- Controlled Substance: NPP is classified as a controlled substance in many countries, and its non-medical use is illegal.
Target Audience
- Medical: Women suffering from advanced breast cancer, osteoporosis, and muscle wasting conditions.
- Bodybuilders and Athletes: Competitive bodybuilders, powerlifters, and athletes who seek to enhance performance and muscle growth (though non-medical use is illegal in many areas).
- Individuals: Those looking to improve muscle strength and recovery after surgery or injury.
Expected Results
- Short-Term: Users may see significant muscle gains, enhanced endurance, and improved overall physical performance within a few weeks.
- Long-Term: Over extended periods, NPP helps improve bone health and density, reduces the risk of fractures, and supports muscle maintenance and growth. Results may vary based on the individual’s health, diet, and exercise regimen.
FAQs
1. What is Nandrolone Phenylpropionate used for?
NPP is used to treat advanced breast cancer, osteoporosis in postmenopausal women, and muscle wasting conditions. It is also used for physique enhancement and muscle growth by athletes and bodybuilders.
2. How is Nandrolone Phenylpropionate administered?
NPP is administered through an intramuscular injection. It is typically injected once a week, but the dosage frequency may vary based on the treatment plan.
3. Are there any side effects of NPP?
Common side effects include virilization in women, acne, increased hair growth, and voice changes. Other effects can include liver toxicity, mood changes, and cardiovascular problems at higher doses.
4. Can NPP be used by men for bodybuilding?
While NPP can be used for physique and performance enhancement, it is not recommended without medical supervision, and its non-prescribed use is illegal in many countries.
5. What are the differences between NPP and nandrolone decanoate?
NPP has a shorter half-life, which requires more frequent injections compared to nandrolone decanoate. Nandrolone decanoate is longer-acting and typically administered less frequently.
6. Is NPP safe for long-term use?
Long-term use can lead to increased risks of side effects, such as liver damage, cardiovascular issues, and virilization in women. It is crucial to follow dosage recommendations and undergo regular health monitoring.


Reviews
There are no reviews yet.